- Details
- By Native News Online Staff
The Coalition of Large Tribes, an organization representing more than 50 tribes with reservations of 100,000 acres or more, signed on to the Navajo Nation’s request for consultation before NASA sends human remains to the moon.
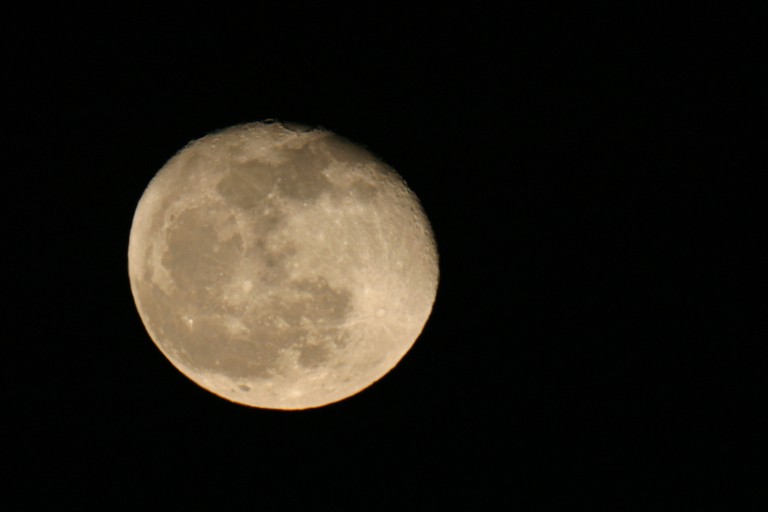
On Jan. 8, NASA has plans to launch a rocket to the moon containing human remains, based on a contract it has with two private companies that make up part of the agency’s commercial arm.
Among the 28 payloads, or cargo on a rocket, going to the moon are some by Celestis and Elysium Space, companies known for providing memorial services by shipping human cremated remains.
Navajo Nation President Buu Nygren wrote a Dec. 21 letter to Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, and Transportation Assistant Secretary for Tribal Government Affairs Arlando Teller objecting to the mission without proper tribal consultation for a sacred place.
“It is crucial to emphasize that the moon holds a sacred position in many Indigenous cultures, including ours,” President Nygren wrote. “We view it as a part of our spiritual heritage, an object of reverence and respect. The act of depositing human remains and other materials, which could be perceived as discards in any other location, on the Moon is tantamount to desecration of this sacred space.”
In his letter, Nygren said this situation was a repeat of an event in the late 90s when NASA sent a rocket carrying the remains of a former astronaut to the moon.
“At the time, Navajo Nation President Albert Hale voiced our objections regarding this action. In response, NASA issued a formal apology and promised consultation with tribes before authorizing any further missions carrying human remains to the Moon,” President Nygren wrote.
On Jan. 4, COLT tribal chairman Marvin Weatherwax sent a similar letter as Nygrens to Buttigieg, Nelson, and Teller.
“As there has been no tribal consultation on the matter, the Coalition of Large Tribes demands that the launch either be delayed or that the cremated remains be removed from the payload until there has been appropriate tribal consultation,” Weatherwax wrote.
“Celestial bodies play an important role in our ceremonial life and cultural heritage for most, if not all Tribes in the United States. NASA has acknowledged this and, on its own website, stated: ‘The Indigenous Peoples Initiative focuses on building relationships across NASA and Indigenous communities through place-based remote sensing training, community engagement, and co-production of knowledge, and yet ignores its own commitment.”
NASA did not respond to Native News Online’s request for comment. But NASA representatives addressed the controversy during a Jan. 4 meeting, according to Space.com.
"We don't have the framework for telling them what they can and can't fly," said Chris Culbert, Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program manager at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. "The approval process doesn't run through NASA for commercial missions."
At the end of his letter, Weatherwax demanded tribal consultation be respected, “even when it is inconvenient.”
More Stories Like This
Chickasaw Lighthorse Police Officer named Indian Country Law Enforcement Officer of the YearIndian Gaming Association Rallies Broad Coalition Against Sports Event Contracts It Calls Illegal Threat to Tribal Sovereignty
Navajo Resources and Development Committee Issues Notice on Livestock Inspection Requirements
American Prairie, Tribal Coalition Files Protest Over Rescinded Grazing Rights
Northern Cheyenne Push Back Against Trump Administration’s Effort to Alter Little Bighorn History
Help us defend tribal sovereignty.
At Native News Online, our mission is rooted in telling the stories that strengthen sovereignty and uplift Indigenous voices — not just at year’s end, but every single day.
Because of your generosity last year, we were able to keep our reporters on the ground in tribal communities, at national gatherings and in the halls of Congress — covering the issues that matter most to Indian Country: sovereignty, culture, education, health and economic opportunity.
That support sustained us through a tough year in 2025. Now, as we look to the year ahead, we need your help right now to ensure warrior journalism remains strong — reporting that defends tribal sovereignty, amplifies Native truth, and holds power accountable.
 The stakes couldn't be higher. Your support keeps Native voices heard, Native stories told and Native sovereignty defended.
The stakes couldn't be higher. Your support keeps Native voices heard, Native stories told and Native sovereignty defended.
Stand with Warrior Journalism today.
Levi Rickert (Potawatomi), Editor & Publisher