- Details
- By Darren Thompson
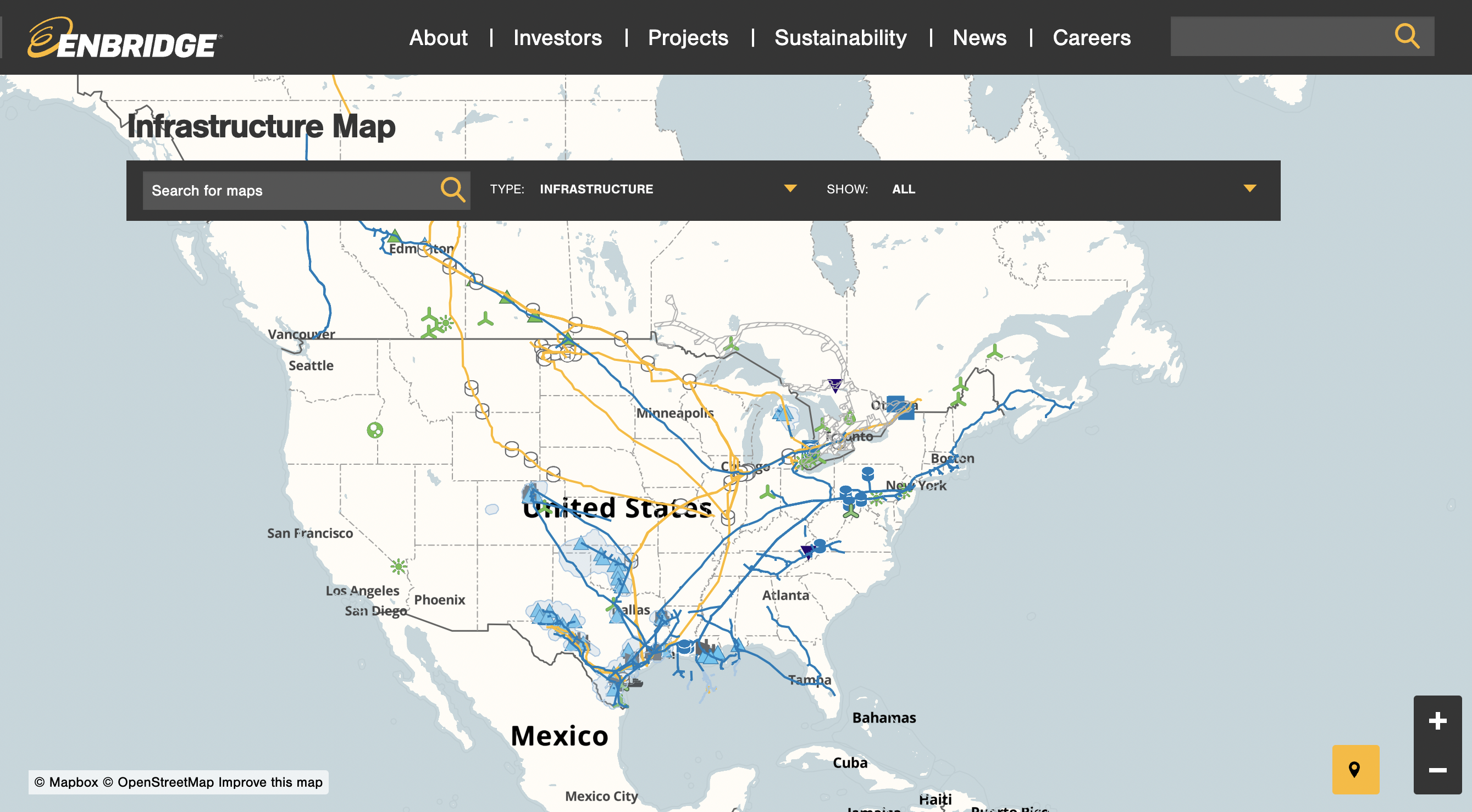
On November 5, the Canadian oil company Enbridge announced that it plans to increase capacity on its pipeline system that connects a crude-oil storage hub in Oklahoma to the Texas Gulf Coast, now that the Line 3 pipeline linking Alberta and Wisconsin is complete. The Carrizo Comecrudo and other Indigenous groups in the area, along with the Indigenous Environmental Network, have pledged to protect Indigenous sacred sites and oppose future pipeline developments.
Increasing capacity may include building a new pipeline linking the Houston area to the Port of Corpus Christi, more than 200 miles away. In October, Enbridge acquired the Ingleside Energy Center in Corpus Christi, Texas, the largest crude-exporting hub in the U.S.
Want more Native News? Get the free daily newsletter today.
Line 3 transports crude oil from the Alberta tar sands to Superior, Wisconsin, through Northern Minnesota. Now that it’s been completed — thanks to approval by the Biden administration on June 23 —its capacity has increased from 390,000 barrels a day to 760,000 barrels a day. Biden’s top domestic policy advisor, Susan Rice, was ordered to divest from the company earlier this year. President Donald Trump initially gave the Line 3 project the green light, and the Biden administration defended it in court when challenged by tribes and environmental groups.
“Returning the line to full capacity sets us up for downstream expansion to the US Gulf Coast,” Enbridge CEO Al Monaco said in the Nov. 5 statement. The company, he explained, wants to continue promoting a "full path access for Canadian heavy [crude oil] to the US Gulf Coast" as the world continues to recover from the pandemic.
Any new pipeline on the Texas coast will be met with resistance from Gulf Coast communities, many of whom have been hit hard by climate disasters intensified by global warming.
“We’ve been fighting Enbridge since pre-NAFTA to protect our sacred sites,” Carrizo Comecrudo Tribal Chairman Juan Mancias told Native News Online. “The wall Trump attempted to build, and any other projects that aimed to extract resources and transport them, have never consulted with tribes in Texas.”
The Carrizo Comecrudo Tribe in South Texas is not a federally recognized tribe, but are the original peyote people, said Mancias. “It was our ancestors who introduced peyote to the Native American Church,” he said. “Our people have always been here, and we predicted these things that are coming, and no one has ever listened to us.”
The three federally recognized tribes in Texas are not native to Texas and were displaced from other locations in the country.
“The Indigenous Peoples of the Coastal Bend will not allow Enbridge to feel comfortable with their colonial ways of destroying Indigenous communities,” the Indigenous Environmental Network said in a statement November 11. “They can expect the same resistance from tribal communities in Texas as they did with Line 3.”
More than 1,000 people have been arrested or issued citations in Minnesota for opposing the construction of Line 3. Opponents object that the pipeline project not only continues to pollute the environment, but threatens wild rice and water in Anishinaabe-ceded territory in northern Minnesota.
Enbridge also completed an expansion of its Wisconsin-to-Illinois Southern Access expansion that starts in Superior, Wisconsin and ends in Flanagan, Illinois, but had been waiting until the completion of Line 3 to return to service. The expansion, which cost nearly $500 million, runs for almost 500 miles. It is part of Enbridge’s larger Mainline network to move Canadian crude oil to refining hubs in the Midwest and Gulf Coast. The expansion was operating at 996,000 barrels per day and is now operating at 1.2 million barrels per day.
Enbridge’s announcement to expand its tar-sands transportation infrastructure further comes weeks after world leaders gathered in Glasgow, Scotland for the global climate summit known as COP26 (the United Nations Climate Change Conference), to discuss plans to address climate change, including the phasing out of fossil fuels.
The company said more pipeline expansions will be needed even after Canada's Trans Mountain Pipeline expansion, which is slated to be completed at the end of 2022, is running.
With the capacity to ship more than 3.1 million barrels a day across 8,600 miles, the Mainline network is Canada's largest crude-oil transporter and exporter, moving crude oil from the Alberta tar sands to the US Midwest refining markets. It is connected to the Cushing, Oklahoma hub and the Gulf Coast through the terminals at Flanagan South in Illinois and Seaway in north Texas. Mainline’s volume averaged 2.67 million barrels per day in the third quarter of 2021, up from 2.56 million barrels per day during the same quarter in 2020. Enbridge projects that it expects to average 2.95 million barrels per day in the fourth quarter of 2000 and nearly 3 million barrels per day in 2022, said in a statement.
More Stories Like This
Gwich'in Tribal Governments Submit Comments Challenging Fish and Wildlife Service's Inadequate Environmental Review of Arctic Refuge Snow RoadRappahannock Tribe Challenges 9M-Gallon Water Plan
Feds release draft long-term plans for Colorado River management
Apache Leader Walks 60 Miles to Court Hearing That Will Decide Fate of Sacred Oak Flat
Rappahannock Tribe Raises Sovereignty and Environmental Concerns Over Caroline County Water Permit
Help us defend tribal sovereignty.
At Native News Online, our mission is rooted in telling the stories that strengthen sovereignty and uplift Indigenous voices — not just at year’s end, but every single day.
Because of your generosity last year, we were able to keep our reporters on the ground in tribal communities, at national gatherings and in the halls of Congress — covering the issues that matter most to Indian Country: sovereignty, culture, education, health and economic opportunity.
That support sustained us through a tough year in 2025. Now, as we look to the year ahead, we need your help right now to ensure warrior journalism remains strong — reporting that defends tribal sovereignty, amplifies Native truth, and holds power accountable.
 The stakes couldn't be higher. Your support keeps Native voices heard, Native stories told and Native sovereignty defended.
The stakes couldn't be higher. Your support keeps Native voices heard, Native stories told and Native sovereignty defended.
Stand with Warrior Journalism today.
Levi Rickert (Potawatomi), Editor & Publisher
