
- Details
- By Drummond Woodsum
Mother Earth is angry. Every day, we read headlines about how climate change-driven natural disasters are wreaking havoc in new and increasingly terrifying ways. Traditional methods of indigenous land stewardship called for living in balance with one another and with the natural world. Such ways of living in symbiosis with nature ensured that preservation of the environment for the benefit of future generations was crucial to any major decisions. The industrial world generally deviated from this way of thinking but the pendulum has swung back in favor of environmental stewardship now that humanity is facing a growing climate crisis.
One way indigenous communities can fight against climate change while simultaneously generating economic development is through sustainable forest management. This is essentially a fancy way of saying that you grow more trees than you harvest, as most tribal forest owners already do. In essence, this means that tribes can produce revenue if they manage their forests in a way that grows trees and, in doing so, produces verifiable “carbon credits” or “carbon offsets”. Those credits may then be sold to buyers. Forest carbon projects have generated hundreds of millions of dollars in revenue for tribes over the past decade. Although the concept of carbon credits is not new, this is a growth trend that appears set to continue for the near future.
What is a carbon credit?
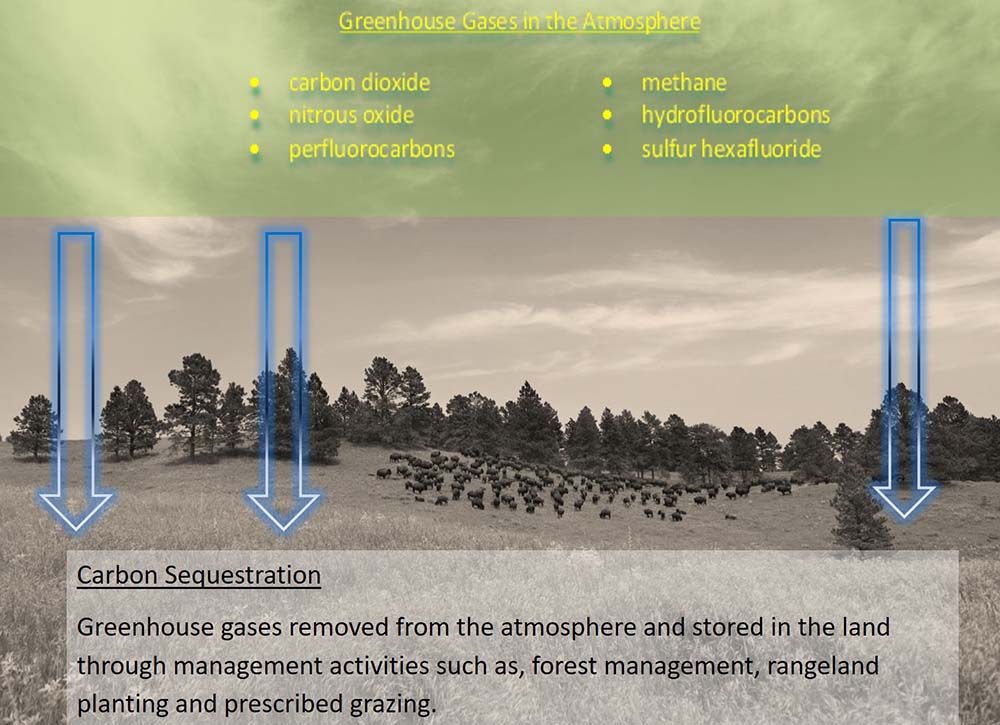
A single carbon credit represents one ton of greenhouse gases (GHGs) removed from the atmosphere. GHGs, are a primary driver of climate change, which are released into the atmosphere through a wide variety of daily activities. For example, GHGs result from agriculture uses, industrial processes such as the creation of motor vehicle fuel, or from the operation of combustion engines, to name a few activities.
How is a carbon credit created?
The good news, amid all this doom and gloom around climate change, is that, if you are a tribal forest landowner, then you are most likely already engaged in an activity that can create carbon credits. Ultimately, a landowner must commit to activities, such as sustainable forest growth, that actively remove GHGs from the atmosphere. One of the best mechanisms to remove GHGs is through forest growth because trees naturally sequester and store carbon (GHGs) through photosynthesis. Do not despair if you missed the lesson on photosynthesis because the bottom line is that the growth of trees that could legally be harvested can result in the creation of carbon credits. The key to carbon credits is “additionality”, meaning that carbon stored in trees could have been released into the atmosphere from logging in the absence of a carbon credit project. Evidence of the carbon storage activities a/k/a tree growth must be documented by a landowner, verified by a third party, and then submitted to a regulatory body for credit issuance. Once issued, carbon credits can be sold to buyers who purchase such credits pursuant to a regulatory compliance plan or a corporate policy aimed at reducing an entity’s “carbon footprint”.
Why should I care about forest carbon?
Popularized in the 2010s by the State of California and embraced as part of the 2016 Paris Climate Accord, carbon credits are a globally recognized mechanism for combatting climate change. Although carbon credits are generated from a range of activities, sustainable forest management is something that many indigenous people have engaged in since time immemorial. Further, federal law already requires tribal nations to manage their forests in a sustainable way. This means that economic opportunity exists just by virtue of engaging in the age-old, traditional activity of environmental stewardship. To top it off, in the best situations, carbon credits can be generated without any curtailing of timber harvesting.
The economic upside is real. Tribally owned forests of varying sizes have been generating tribal revenue for over a decade now. Some of the numbers can be astonishing. Tribal landowners east to west across Indian country have generated significant revenue, ranging from the millions to more than one hundred million dollars. Tribal carbon revenues have supported land acquisition, community investment, and tribal businesses. All from growing and measuring the same trees that we have protected for generations.
Help us defend tribal sovereignty.
At Native News Online, our mission is rooted in telling the stories that strengthen sovereignty and uplift Indigenous voices — not just at year’s end, but every single day.
Because of your generosity last year, we were able to keep our reporters on the ground in tribal communities, at national gatherings and in the halls of Congress — covering the issues that matter most to Indian Country: sovereignty, culture, education, health and economic opportunity.
That support sustained us through a tough year in 2025. Now, as we look to the year ahead, we need your help right now to ensure warrior journalism remains strong — reporting that defends tribal sovereignty, amplifies Native truth, and holds power accountable.
 The stakes couldn't be higher. Your support keeps Native voices heard, Native stories told and Native sovereignty defended.
The stakes couldn't be higher. Your support keeps Native voices heard, Native stories told and Native sovereignty defended.
Stand with Warrior Journalism today.
Levi Rickert (Potawatomi), Editor & Publisher
